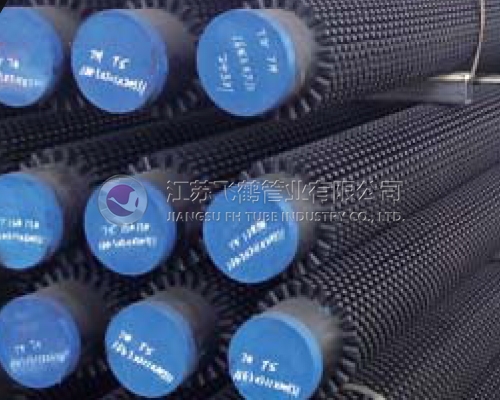
U-bent Tube
- Detailed introduction
U-shaped heat exchange tube, also known as U-tube heat exchanger, is a kind of shell and tube heat exchanger. It is composed of tubesheet, shell, tube bundle and other parts.
Under the same diameter, the U-tube heat exchanger has the largest heat exchange area; it has simple structure, compact structure, high sealing performance, convenient maintenance and cleaning, minimum metal consumption under high temperature and high pressure, and the lowest cost; the U-tube heat exchanger has only one tube sheet, which has good thermal compensation performance and strong pressure bearing capacity, and is suitable for operation under high temperature and high pressure conditions.

Structure
The main structure of U-tube heat exchanger includes tube box, cylinder, head, heat exchange tube, connecting pipe, baffle plate, anti impact plate and guide tube, anti short circuit structure, support and other accessories of tube shell side.
Heat exchange tube
1. Common heat exchange tube
The former is suitable for heat transfer without phase change and easy vibration, and the latter is suitable for reboiler, condensation heat transfer and vibration free general occasions.
There are various forms of heat exchange tube, smooth tube is the most traditional form, because it has the advantages of easy manufacture and low cost per unit length, it is the most common in current application. The pipe should be able to withstand a certain temperature difference and stress. When the fluid in the tube side and shell side is corrosive, the pipe should also have corrosion resistance.
The following series of heat exchange tube lengths are recommended: 1.0m, 1.5m, 2.0m, 2.5m, 3.0m, 4.5m, 6.0m, 7.5m, 9.0m, 12.0m. For a certain heat exchange area, the longer heat exchange tube is more economical, so the heat exchanger in engineering is generally slender structure. However, if the heat exchange tube is too long, it will not be conducive to the installation and maintenance of the heat exchanger.
The material sources of pipes are very wide, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass and their alloys, copper nickel alloy, nickel, titanium, graphite, glass and other special materials. In addition to single material manufacturing, composite tubes are often used to meet the production requirements.
2. High efficiency heat exchange tube
In order to enlarge the effective heat transfer area inside and outside the tube at the same time or to enhance the heat transfer coefficient of the tube side to the greatest extent, the inner and outer surfaces of the heat exchange tube are rolled into various surface shapes, or the disturbing elements are inserted into the tube to make the fluid inside and outside the tube turbulent at the same time and improve the performance of the heat exchange tube. According to the shape of heat exchange tubes and the mechanism of heat transfer enhancement, the tubes can be divided into rough surface tubes, finned tubes, self-supporting tubes and plug-in tubes.
Most of the high efficiency heat exchange tubes have the function of heat transfer enhancement both inside and outside the tubes. According to different working conditions, the ideal heat transfer effect can be achieved by using different combinations of high efficiency heat exchange tube and new tube bundle support.